Summary and Setup
This lesson shows how to use Python and scikit-image to do basic image processing.
Prerequisites
This lesson assumes you have a working knowledge of Python and some previous exposure to the Bash shell. These requirements can be fulfilled by: a) completing a Software Carpentry Python workshop or b) completing a Data Carpentry Ecology workshop (with Python) and a Data Carpentry Genomics workshop or c) independent exposure to both Python and the Bash shell.
If you’re unsure whether you have enough experience to participate in this workshop, please read over this detailed list, which gives all of the functions, operators, and other concepts you will need to be familiar with.
Before following the lesson, please make sure you have the software and data required.
Before joining the workshop or following the lesson, please complete the data and software setup described in this page.
Data
The example images used in this lesson are available for University
of Birmingham staff on SharePoint. Please follow this link,
log on if required, and click “Download”. Unzip the downloaded file, and
save the contents as a folder called data somewhere you
will easily find it again, e.g. your Desktop or a folder you have
created for using in this workshop. (The name data is
optional but recommended, as this is the name we will use to refer to
the folder throughout the lesson.)
Software
Download and install the latest Miniforge distribution for your operating system. Make sure to choose the version with Python 3.10 in the base environment.
-
Use Mamba to make a new environment for this Lesson and install the necessary packages. To do this open a terminal (or Miniforge3 Prompt if using Windows) and run the following commands:
mamba update --all --yes mamba create -y -n image-env -c conda-forge python=3.9 mamba activate image-env mamba install -y -c conda-forge scikit-image ipympl napari pyqt jupyterlabLaunch the Miniforge3 Prompt program and run your commands within this. (Running mamba commands on the standard Command Prompt may return an error:
'mamba' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.) -
Open a Jupyter notebook:
Open a terminal (or Miniforge3 Prompt if using Windows), activate your environment and open Jupyter Lab:
mamba activate image-env jupyter labAfter Jupyter Lab has launched, click the “Python 3” button under “Notebook” in the launcher window, or use the “File” menu, to open a new Python 3 notebook.
-
To test your environment, run the following lines in a cell of the notebook:
PYTHON
import imageio.v3 as iio import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import skimage as ski import napari %matplotlib widget # load an image image = iio.imread(uri='data/colonies-01.tif') # rotate it by 45 degrees rotated = ski.transform.rotate(image=image, angle=45) # display the original image and its rotated version side by side fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2) ax[0].imshow(image) ax[1].imshow(rotated) # open the image in Napari viewer = napari.Viewer() viewer.add_image(data=image, name="colonies_01", rgb=True)Upon execution of the cell, a figure with two images should be displayed in an interactive widget. When hovering over the images with the mouse pointer, the pixel coordinates and colour values are displayed below the image. It will also open a Napari Viewer and display an image within it.
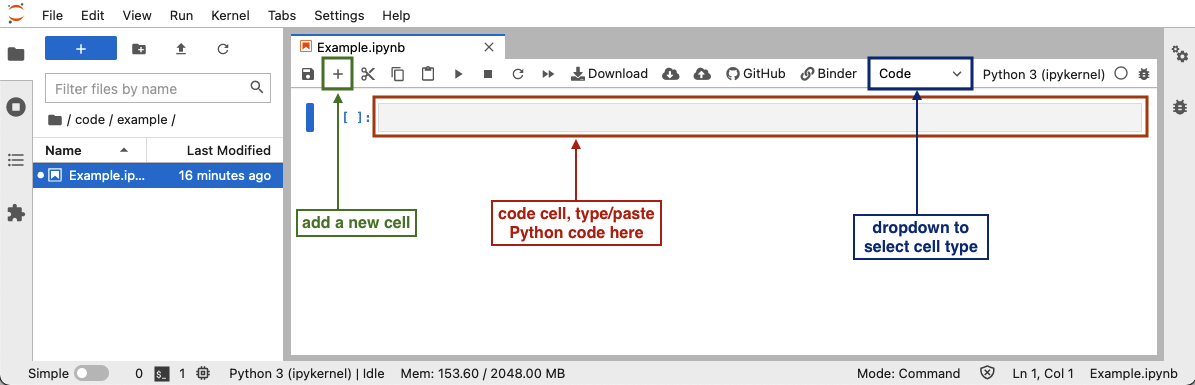 To
run Python code in a Jupyter notebook cell, click on a cell in the
notebook (or add a new one by clicking the
To
run Python code in a Jupyter notebook cell, click on a cell in the
notebook (or add a new one by clicking the +button in the toolbar), make sure that the cell type is set to “Code” (check the dropdown in the toolbar), and add the Python code in that cell. After you have added the code, you can run the cell by selecting “Run” -> “Run selected cell” in the top menu, or pressing Shift+Enter.This lesson uses Matplotlib features to display images, and some interactive features will be valuable. To enable the interactive tools in JupyterLab, the
ipymplpackage is required.Theipymplbackend can be enabled with the%matplotlibJupyter magic. Put the following command in a cell in your notebooks (e.g., at the top) and execute the cell before any plotting commands.If you are using an older version of JupyterLab, you may also need to install the labextensions manually, as explained in the README file for the
ipymplpackage. A small number of exercises will require you to run commands in a terminal. Windows users should use PowerShell for this. PowerShell is probably installed by default but if not you should download and install it.
